Ladle, also known as steel ladle, steel ladle, ladle, etc., is a container for storing, transporting and processing molten steel, and is an important equipment for refining tasks. Ladle has two main functions: the first is to receive molten steel; the second is refining outside the furnace. With the diversification of secondary refining, the consumption of refractory materials is relatively high and the service life is also shortened. In the late 1970s, in order to reduce resource consumption and labor intensity, the method of casting refractory materials was gradually adopted in the lining of the ladle.
Amorphous refractory materials are basically used more or less in thermal equipment and kilns in all industrial fields. In recent decades, refractory materials for ladles have experienced rapid development from shaped to amorphous and then to castable materials.
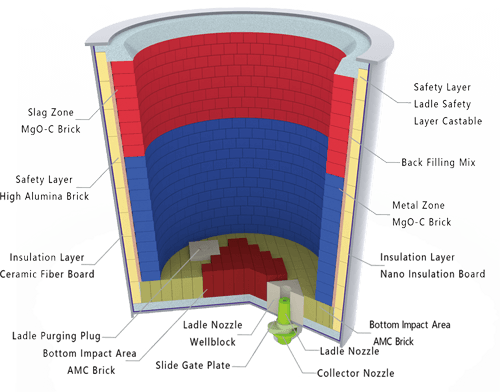
- The refractory materials of ladle lining are generally divided into four parts: insulation layer refractory materials, permanent layer refractory materials, working layer refractory materials, and functional refractory materials.
- The insulation layer refractory materials play a role of insulation, and are generally lightweight insulation materials, such as lightweight clay bricks, aluminum silicate fiberboards, lightweight coatings, lightweight porous castables, nano-reflective insulation boards, etc.
- The permanent layer refractory materials are also called safety layer refractory materials. They mainly play an insurance role to prevent the molten steel that leaks through after the working layer refractory materials are damaged and burn the metal shell, ensuring the safety of use. The main materials of permanent layer refractory materials are: high-alumina bricks, aluminum-magnesium castables, high-alumina castables, etc. The working layer refractory materials are in direct contact with the slag and molten steel in the ladle, and they must be able to withstand the high-temperature erosion of slag and the scouring of molten steel. The service life of the ladle is determined by the mechanical scouring of the molten steel on the working layer refractory materials and the process level of this layer. The working layer refractory materials have gone through different stages such as clay bricks, high-alumina bricks, wax stone bricks, carbon-free, low-carbon, and special refractory materials.
- Unshaped refractory materials for ladles have always been the focus of long-term attention of the refractory industry at home and abroad. With the development of refractory materials, refractory materials for ladles at home and abroad have also experienced different development periods. At the beginning, the lining bricks of ladles abroad were mainly high-alumina bricks; in the 1970s and 1980s, medium and low-grade aluminum-magnesium-carbon (Al-Mg-C) bricks were mainly used. In recent decades, in order to reduce the consumption of refractory materials and reduce costs, many measures have been taken and good results have been achieved. For example, before the 1990s, ordinary Japanese ladles used relatively low-priced zircon bricks, wax stone bricks, and high-silica bricks with a SiO2 content of 85%; in the late 1990s, some Japanese ladles had been constructed by integral casting, and the utilization rate of this method has accounted for about 95% so far. Today, the main refractory material used in Japan is spinel castable, which has good resistance to slag erosion and slag penetration.
- The production line of a certain continuous casting machine built by a foreign company had a service life of only 6 furnaces per ladle at the beginning. After continuous testing and improvement, the service life can now reach 160 furnaces, and the cost of use has also been reduced by about 40%.
- From the founding of the People’s Republic of China to before the reform and opening up, the domestic refractory materials for ladles were mainly aluminum silicate products; since the 1980s, China has gradually developed a number of different types of refractory materials for ladles, such as magnesium calcium (carbon) and aluminum magnesium (carbon). Aluminum magnesium (carbon) refractory materials account for the majority of specifications and varieties, becoming the main refractory materials for ladles in my country. Since the early 1990s, my country has successively carried out research and application of corundum-spinel castables and alumina-spinel castables, and achieved good results. As the lining material of the ladle, the aluminum-magnesium refractory castable must have excellent performance in terms of anti-scaling and erosion resistance. However, since it must be used for a long time in an environment above 1600℃, vitrification will occur near its working surface due to over-sintering and slag penetration, which makes it difficult to ensure its durability. Adding a certain amount of magnesium oxide fine powder in the batching process can effectively improve some properties of alumina-magnesia spinel castables. Magnesium oxide in magnesia sand and aluminum oxide in the material will generate in-situ spinel at high temperatures, thereby strengthening the internal structure of the material, improving slag resistance and inhibiting slag penetration, thereby greatly extending the service life of the ladle. Since Al2O3 and MgO react at high temperatures to generate in-situ spinel, the sample becomes loose and has fine structures inside, so this type of ladle has better durability.
- With the development and application of synthetic magnesia-alumina spinel materials, carbon-containing refractory materials and the development and progress of low-cement, ultra-low-cement and cement-free refractory castable technologies, a new generation of alumina/magnesia/graphite-based refractory materials has begun to be used in many steelmaking containers, among which the most common application is in ladles.

More details about Ladle Furnace
What is ladle furnace slag used for?
It is generally used in construction materials, soil rejuvenation, and CO2 capture. This paper reviews the production process, the mineralogical and morphological properties, stabilization techniques, and the applications of ladle furnace (LF) slag.
What is the function of LRF?
LRF is used to desulfurize steel, remove other impurities, and maintain molten steel for casting operations. 5. The ladle refining furnace also plays a buffer role between the steelmaking furnace and the continuous casting machine, which reduces the casting cost and makes the steelmaking operation more flexible.
What are the reactions in the ladle furnace?
Deoxidation reactions carried out in the ladle are exothermic and thus raise the temperature of the liquid steel, but the steel also loses heat by radiation from the top surface, by heating of the ladle lining, and by heat flux through the lining and shell.
What is a ladle heating furnace?
The ladle furnace (LF) makes it possible to divide the steel melting operations, carried out in EAF, from those of treatment and refining. The liquid steel produced by the EAF is poured into the ladle, which serves as a reactor for metallurgical operations at the treatment stations.