Short process steelmaking in electric furnaces is a new process for steel production with scrap as the main raw material. The electric furnace consists of furnace body and furnace cover, the shell of the furnace body is made of steel plate, and the inner lining is made of refractory material. The outer ring of the furnace cover is made of steel, mostly water-jacketed, and the top, except for water-cooled, is made of refractory material. Electric furnace steelmaking mainly uses electric arc radiation heating, sometimes blowing heavy oil or oxygen to accelerate the melting. The temperature inside the electric furnace is high, the atmosphere changes greatly, and the smelting cycle is relatively short.
Electric Furnace Lining
The electric furnace lining is often subject to slag erosion and to the scouring of molten steel, slag and dust gases. In addition, they are subjected to high-temperature heat radiation, which is particularly prominent in some hot spots on the furnace wall. Furnace roof and furnace lining in the opening lid, repair furnace and charging will also be subject to great thermal shock and impact, the working environment is very harsh. Due to the different parts of the electric furnace lining, the working environment and damage of each part are also very different.
Electric Furnace Covers
The electric furnace cover (roof) is a spherical structure with electrode holes and exhaust holes, the outer ring part is called the main furnace whisker, the middle part is called the small roof, the roof can be lifted or rotated for charging. The working conditions of the electric furnace cover are extremely harsh, and a large amount of heat energy is reflected from the liquid surface and the furnace lining to the cover, making the temperature of the cover sometimes as high as 1700℃ or more. Its temperature change is also very sharp, during the charging period, in 15~20s, the cover temperature will be from 1600~1650 (sharp drop to 500~600 ℃, thermal erosion is very serious. Others are slag, lime and fluorite powder surface, furnace gas and soot, such as chemical erosion, as well as the cover lifting, lowering and furnace tilting on its mechanical vibration, which play a large degree of destruction of the cover, seriously affecting the life of the cover.
Among them, the damage of the main furnace roof is mainly due to high temperature and slag splashers. Previously, the use of silica brick roof, the splash of CaO, SiO and iron oxide will react with it to form a low melting point material, molten spalling, serious damage. Changed to high alumina bricks, magnesium chrome bricks and other refractory materials for the top of the furnace, the melt flow phenomenon is less, but only in the formation of metamorphic layer on the working surface and thermal spalling phenomenon.
Small furnace roof lining damage in addition to the main roof damage, but also by high temperature heat radiation, as well as electrode holes, exhaust holes on the structure of the adverse effects. In addition, it will be subjected to high-speed airflow and furnace dust scouring.
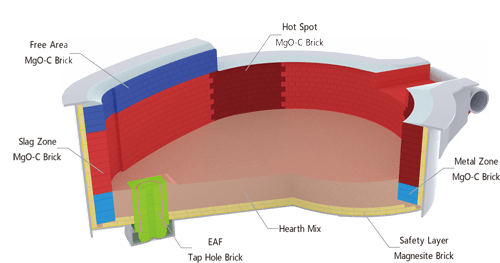
Fireplace wall
Furnace walls can be categorized into ordinary furnace wall areas, slag line areas and hot spots according to different working environments.Furnace walls are often subjected to high temperatures and rapid changes in temperature, but also to direct scouring of the liquid steel, chemical erosion of the slag, as well as mechanical collision of the charge and other thermal shocks.
Erosion damage is particularly severe near the slag line area. Slag containing FeO, CaO, SiO and a small amount of Al, as well as furnace dust sprayed onto the furnace wall, and the furnace wall lining fusion, and gradually to the lining refractory material in the pore penetration, the surface layer is slagging, and then due to mechanical reasons or thermal shock and peeling.
Furnace wall parts of the temperature distribution is very uneven, in which the three-phase electrode corresponding to the area of high temperature, that is, the hot spot, the part in addition to the slag and steel erosion, but also to withstand the arc direct high temperature radiation, resulting in the lining of the furnace loses the speed of increasing damage to the accelerated. Sometimes the part of the temperature up to 2000 ℃, especially the 2nd electrode, is the weak link of the furnace wall. If the use of ultra-high-power electric furnace transformer, hot spot parts of the furnace wall damage is more serious.
Bottom of the furnace
The bottom of the furnace bottom consists of three parts: the insulation layer, the bricklaying layer and the knotted layer.
The insulation layer is used to reduce the heat loss through the bottom of the furnace, the bricklaying layer mainly serves to ensure the solidity of the molten pool part and prevent the leakage of steel, and the knotted layer is in direct contact with the liquid steel and slag, which is the working layer of the bottom of the furnace. Furnace bottom and embankment slope together constitute the molten pool, its lining damage and the working environment is mainly steel and slag chemical erosion, as well as high-temperature radiation and convection heat loss, as well as charging mechanical impact, etc., the damage is also very serious.
Commonly used refractory materials for electric furnaces are magnesium bricks, dolomite bricks, high alumina bricks, silica bricks and magnesium sand knotting materials, etc. However, due to the different working environments of each part of the electric furnace, the refractory materials should be selected according to the specific use of the environment and the choice of suitable refractory materials.